Copper compression fittings are a popular and reliable solution for connecting copper pipes without the need for soldering or welding. They are widely used in plumbing, HVAC, and mechanical systems because of their ease of installation and dependable sealing performance.
These fittings are commonly found in residential and commercial plumbing systems, as well as heating and cooling applications, where quick, clean, and secure pipe connections are required. Their versatility makes them ideal for both new installations and repair work.
The purpose of this article is to help readers understand what copper compression fittings are, explore the different types available, and learn where and how each type is typically used. Whether you are a homeowner, DIY enthusiast, or plumbing professional, this guide will provide valuable insight.
What Are Copper Compression Fittings?
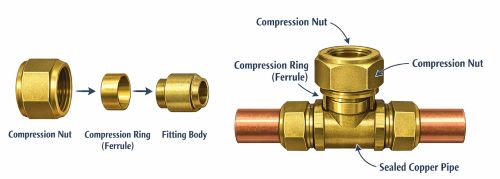
Copper compression fittings are mechanical pipe connectors designed to join copper tubing by compressing a ring (ferrule) against the pipe to create a tight seal. Unlike soldered fittings, they do not require heat, making them safer and easier to install in many situations.
A compression fitting consists of three main parts: a nut, a ferrule, and a fitting body. The ferrule is compressed onto the copper pipe when the nut is tightened. This compression creates a strong, leak-resistant seal between the pipe and the fitting body.
When compared to Soldered fittings, this type of fitting requires heat, flux, and solder to bond pipes together permanently. Compression fittings, on the other hand, rely on mechanical pressure and can often be removed or adjusted. This makes compression fittings ideal for repairs, modifications, and locations where open flames are not permitted.
Key Components of Copper Compression Fittings
Understanding the components of a compression fitting helps ensure proper installation and long-term performance.
1. Compression Nut
The nut is threaded and tightens onto the fitting body. Its primary function is to apply pressure to the ferrule, forcing it to compress against the pipe.
2. Compression Ring (Ferrule)
The ferrule is a small metal ring that sits between the nut and the fitting body. When compressed, it grips the copper pipe and creates a watertight seal.
3. Fitting Body
The fitting body is the main structure that connects pipes or transitions between different components. It provides the surface against which the ferrule is compressed.
4. Creating a Leak-Proof Seal
When properly installed, the combined action of the nut, ferrule, and fitting body creates a durable seal that resists leaks, even under pressure.
Types of Copper Compression Fittings
Here are the types of Copper compression fittings:
1. Straight Compression Fittings
Straight compression fittings are designed to connect two copper pipes in a straight line. They are commonly used to extend pipe runs or join two sections of tubing.
Typical applications include:
➡️ Water supply lines
➡️ Heating systems
➡️ Appliance connections
2. Compression Elbows
Compression elbows allow pipes to change direction, typically at 90 degrees or 45 degrees. They are especially useful in tight spaces where bending copper tubing is impractical.
Advantages include:
➡️ Clean directional changes
➡️ Reduced stress on pipes
➡️ Easier installation in confined areas
3. Compression Tees
Compression tee fittings are used to split or combine water flow by connecting three pipes at a junction.
Common uses:
➡️ Branching water supply lines
➡️ Bathroom and kitchen plumbing
➡️ Commercial piping systems
4. Compression Couplings
Compression couplings are similar to straight fittings but are often used specifically for repairs or extensions.
Key uses include:
➡️ Fixing damaged pipe sections
➡️ Extending existing copper lines
➡️ Replacing corroded joints
5. Compression Adapters
Compression adapters allow copper pipes to connect to threaded components.
Types include:
➡️ Male threaded adapters
➡️ Female threaded adapters
These fittings are often used to connect copper pipes to valves, faucets, or fixtures made from brass, steel, or plastic.
6. Compression End Caps and Plugs
End caps and plugs are used to seal the end of a copper pipe.
Applications include:
➡️ Temporary pipe closures during renovations
➡️ Permanent sealing of unused pipe runs
➡️ Maintenance and system testing
Common Materials Used in Copper Compression Fittings
Here are the common materials used in Copper compression fittings:
1. Brass Compression Fittings
Brass is the most commonly used material due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with copper pipes.
Pros:
➡️ Durable and long-lasting
➡️ Corrosion-resistant
➡️ Widely available
Cons:
➡️ Higher cost than some alternatives
2. Copper Compression Fittings
Copper fittings are sometimes used for uniform material compatibility.
Pros:
➡️ Excellent corrosion resistance
➡️ Ideal for potable water systems
Cons:
➡️ Softer material, less common than brass
Sizes and Standards of Copper Compression Fittings
Copper compression fittings are available in a wide range of sizes to match standard copper pipe diameters.
Common pipe sizes include:
➡️ 1/4 inch
➡️ 3/8 inch
➡️ 1/2 inch
➡️ 3/4 inch
Metric vs. Imperial Sizing
Some systems use metric sizing, while others use imperial measurements. Selecting the correct standard is critical for ensuring a proper fit.
Importance of Correct Sizing
Incorrect sizing can lead to leaks, poor sealing, and system failure. Always verify pipe diameter before choosing a fitting.
Applications of Copper Compression Fittings
Copper compression fittings are used across multiple industries, including:
1. Residential plumbing systems
2. Commercial and industrial plumbing
3. HVAC installations
4. Gas and water supply lines
Their versatility makes them suitable for both permanent installations and temporary connections.
Advantages of Using Copper Compression Fittings
The following are the advantages of using Copper compression fittings:
1. No soldering or heat required
2. Quick and straightforward installation
3. Easy to disassemble or adjust
4. Ideal for tight or enclosed spaces
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their advantages, compression fittings are not suitable for every application.
Considerations include:
➡️ Not ideal for high-vibration environments
➡️ May loosen over time if improperly installed
➡️ Over-tightening can damage the ferrule or pipe
Long-term dependability depends on proper installation and routine inspection.
Installation Tips and Best Practices
Below are the tips and best practices for installation:
1. Cut pipes cleanly and remove burrs
2. Ensure correct ferrule placement
3. Tighten the nut gradually and evenly
4. Avoid over-tightening
Use pipe sealant or tape only on threaded connections, not on compression joints
Choosing the Right Copper Compression Fitting
When selecting a fitting, consider:
➡️ System pressure and temperature
➡️ Environmental conditions
➡️ Pipe material compatibility
For complex systems or gas lines, consulting a licensed professional is strongly recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are copper compression fittings reusable?
In some cases, they can be reused, but replacing the ferrule is often recommended for a secure seal.
Can compression fittings be used on hot water lines?
Yes, most compression fittings are suitable for hot water applications when properly rated.
How long do compression fittings last?
With correct installation and maintenance, compression fittings can last decades.
Conclusion
Copper compression fittings offer a practical, efficient, and versatile solution for connecting copper pipes. From straight fittings and elbows to tees, adapters, and end caps, each type serves a specific purpose in plumbing and HVAC systems.
By selecting the correct fitting, using proper installation techniques, and choosing high-quality materials, you can ensure long-lasting, leak-free performance. Investing in the right copper compression fittings is a smart choice for both professionals and DIY users seeking reliability and durability.
Post time: Jan-15-2026