In industries ranging from oil and gas to plumbing and chemical processing, pipe fittings are crucial components. They ensure the safe and reliable transport of fluids and gases under varying pressures and temperatures.
Whether you’re assembling a water line or designing a high-pressure hydraulic system, getting the connection right is everything—and this is where NPT threads come into play.
What Are NPT Threads?
NPT stands for National Pipe Taper, a standardized thread used in North America for joining pipes and fittings. What sets NPT threads apart is their tapered design, which forms a tight, leak-resistant seal. In this article, we’ll dive deep into why the NPT thread taper angle matters and how it affects the performance and safety of your system.
What Is NPT Thread Taper Angle?
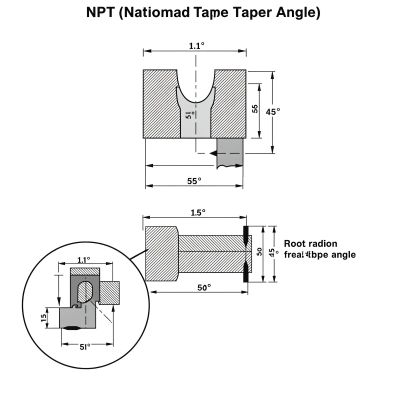
NPT threads are tapered pipe threads standardized by ANSI/ASME B1.20.1. Unlike straight threads, which have a uniform diameter throughout, NPT threads gradually decrease in diameter along the length of the thread.
Standard Taper Angle: 1° 47′
The taper angle of an NPT thread is 1° 47′ (1.7899° per side). This means each side of the thread tapers inward at this precise angle to create a wedging effect when mated with another fitting.
The 1:16 Taper Ratio
This angle corresponds to a 1:16 taper, meaning that for every 16 units of length, the diameter decreases by 1 unit. This subtle taper is what allows NPT threads to form a pressure-tight seal.
The Function of Taper in Pipe Threads
How Taper Creates a Seal
The taper in NPT threads causes the male and female threads to interlock tightly as they are screwed together. As the threads engage, they deform slightly, compressing against each other to create a mechanical seal.
Comparison with Straight Threads
Straight threads rely on an O-ring or gasket to seal. In contrast, NPT threads seal by interference fit—meaning the tightness and seal come from the threads themselves, not just an external sealant.
Thread Engagement and Deformation
The success of the seal depends heavily on how well the threads engage and deform. A proper taper ensures full contact and compression, which leads to a tight seal that can withstand pressure and vibration.
Why Taper Angle Precision Is Critical
Poor Taper Equals Poor Seal
Even a small deviation from the correct taper angle can lead to poor thread engagement, compromising the sealing function. This can cause minor leaks or even catastrophic failures.
Leak Risk
If the taper angle is too shallow or too steep, the threads may not compress correctly, leaving gaps for fluid or gas to escape. This is particularly dangerous in high-pressure or hazardous environments.
Stress and Strain Distribution
An accurate taper angle helps distribute mechanical stress evenly along the threads. Incorrect tapering can result in localized stress, increasing the chance of thread stripping or cracking under pressure.
Industry Standards and Compliance
ASME B1.20.1: The Guiding Standard
The ASME B1.20.1 standard defines the correct dimensions and tolerances for NPT threads. Manufacturers must follow these specifications to ensure safe and reliable fittings.
Why Standards Matter
Adhering to these standards is not optional—it’s a necessity for safety, performance, and legal compliance. Fittings that don’t meet spec can cause system failure, downtime, and liability issues.
Quality Control and Inspection
Inspection tools are used to verify that the taper angle is within specification. Taper gauges and thread measuring tools are common in production environments to catch any out-of-spec parts before they’re installed.
Real-World Applications and Consequences
Industries That Rely on NPT Threads
➡️ Oil & Gas: Sealing pressurized fluids
➡️ Plumbing: Water and waste systems
➡️ Hydraulics: High-pressure fluid systems
➡️ Chemical Processing: Preventing leaks in hazardous environments
What Happens When It Goes Wrong?
Imagine a gas line in a chemical plant leaking because of an improperly cut thread taper. Not only does it risk product loss, but it can also lead to fires, explosions, or regulatory fines.
Cost of Failure
The financial impact of ignoring taper precision can include:
➡️ Equipment damage
➡️ Downtime
➡️ Maintenance costs
➡️Safety violations
➡️ Legal claims
Tools and Methods for Measuring Taper Angle
Common Tools
➡️ Taper Gauges: For quick, visual checks
➡️ Thread Measuring Wires: For precision checking of pitch diameter
➡️ CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines): For exact taper angle measurements in manufacturing environments
Best Practices
➡️ Always verify threads before installation
➡️ Use calibrated tools
➡️ Train technicians to identify signs of improper taper
FAQ Section
Q: Can I use NPT threads on straight-thread fittings?
A: No, NPT threads are tapered and are not compatible with straight threads without an adapter.
Q: What happens if the taper angle is off?
A: The thread may not seal properly, leading to leaks or mechanical failure under pressure.
Conclusion
The NPT thread taper angle is more than a minor detail—it’s the key to a leak-proof, pressure-resistant joint. Precision in this angle ensures proper sealing, structural integrity, and system reliability.
In any industry that depends on pipe fittings, attention to taper angle is non-negotiable. Following the standards, using the right tools, and respecting the design geometry can save you from costly mistakes.
Before your next installation or inspection, make sure your fittings are made to spec, and that you or your team are using the proper tools to confirm taper angle accuracy.
Post time: May-15-2025